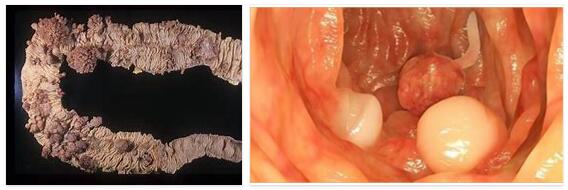
In the familial adenomatous polyposis is a disorder that takes place their inheritance autosomal dominant manner. The colon is attacked by polyps, which lead to colon cancer.
What is familial adenomatous polyposis?
According to Foodezine, familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant disease in which multiple adenomatous polyps develop in the colon. FAP is one of the hereditary diseases caused by genetic defects. Familial adenomatous polyposis means that children of the parents concerned have a risk of more than 50 percent of the same disease if the other parent is not affected.
However, this information cannot be provided in around a third of all patients. It is therefore assumed that the genetic defect is re-induced by itself. Polyps within the intestine develop in adolescents. At first they are still benign. In the further course, however, they degenerate viciously.
With familial adenomatous polyposis, there is almost a 100 percent chance of developing colon cancer. FAP has a share of around one percent among the types of colon cancer. Familial adenomatous polyposis is considered a rare disease. It is estimated that around five to ten in 100,000 people are affected by the gene mutation.
Causes
The cause of familial adenomatous polyposis is a mutation of the APC gene. This gene plays an important role within the degradation complex of ß-catenin. It is also important for the structure of the mitotic spindle. If a mutation occurs in the gene, this slows down ß-catenin ubiquitination.
This involves transferring the protein ubiquin to a target molecule. For this reason, the ß-catenin is no longer broken down correctly by the proteasomes, which means that it accumulates and is responsible for increasing proliferation (rapid growth of tissue). Because the degradation of the mitotic spindle is also involved, this results in a malfunction of the APC gene, which is noticeable in the frequent maldistribution of chromosomes. This leads to a malignant degeneration of the tissue.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
The first symptoms appear in familial adenomatous polyposis between 10 and 25 years of age. In most cases, the disease goes unnoticed at first. Later, symptoms such as constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, the discharge of blood or mucus, abdominal pain and pain in the rectum become noticeable.
Furthermore, the patients often suffer from weight loss. Attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis (AFAP) is a milder variant of FAP. It shows up in later years of life and has fewer polyps than FAP. Ultimately, however, the risk of developing colon cancer is just as high as that of familial adenomatous polyposis.
Some patients may experience benign changes outside of the colon that show before the colon polyps form. They are considered an indication of FAP. Therefore, they should always be carefully examined.
Diagnosis
If familial adenomatous polyposis is suspected, a doctor should be consulted. They can diagnose the disease by performing a colonoscopy and taking a tissue sample (biopsy).
If the patient is at risk, it is recommended that they undergo regular colonoscopy from the age of 10. This usually takes place every year. If a rectosigmoidoscopy is performed, the doctor looks at the lower part of the intestine, which is not painful for the patient.
For this reason, no anesthesia is necessary, even with children. Before the examination, the patient is given a minor enema. If there is a mild form of FAP, a complete colonoscopy is usually used. The same applies to a polyp finding after a rectoscopy.
This procedure can be used to determine whether there are polyps in the rest of the intestine. Colonoscopy is considered more uncomfortable than rectosigmoidcopy because it can cause pain. Therefore, patients are given a sedative beforehand. Familial adenomatous polyposis causes colon polyps to degenerate into colon cancer in 70 to 100 percent of all patients. The only way to avoid this is to surgically remove the bowel.
Complications
Familial adenomatous polyposis can lead to various complications. In the worst case, the affected person suffers from colon cancer in the course of the disease and can die from it. Colon cancer itself can also lead to further complaints and complications.
Unfortunately, the symptoms go unnoticed at first, so that a diagnosis cannot be made early and the disease is usually only discovered by chance. Discomfort in the stomach and abdomen only occurs in adulthood. Most patients suffer from severe gas, constipation and diarrhea. It is not uncommon for abdominal pain to occur.
Just as often the finish is bloody and slimy, which can trigger a panic attack in many people. This results in weight loss and, in many cases, dehydration. There are no complications in the diagnosis, this is carried out in the form of a colonoscopy.
Treatment then usually takes the form of an operation in which the bowel is removed. The person concerned is dependent on an artificial outcome, which significantly reduces the quality of life and can lead to severe psychological complaints. These symptoms mainly occur when the patient is very young.
When should you go to the doctor?
This disease must always be examined and treated by a doctor. If there is no treatment, the disease can lead to the development of colon cancer and thus to the death of the patient. An early diagnosis enables early treatment and thus the chances of a positive course of the disease.
A doctor should be consulted if the patient has stomach upset or bowel problems that persist for a long time. These include above all diarrhea or constipation, which can also lead to flatulence or severe pain in the abdomen.
An immediate examination is necessary if the person has bloody stools. As a rule, the symptoms appear very frequently, but cannot be assigned to an allergy or an intolerance. In most cases, the diagnosis of the disease is made by an internist.
The disease can be diagnosed relatively easily with the help of a colonoscopy. In most cases, further treatment is also carried out by an internist or surgeon. The further course of the disease depends very much on its progression.
Treatment & Therapy
Once familial adenomatous polyposis has been confirmed, the doctor usually recommends removing the colon and rectum. There are three surgical procedures available for this purpose. This includes the proctocolectomy with an ileopuchanal anastomosis. The rectum and large intestine are removed while the sphincter is retained.
The patient is given an artificial anus for about three months. The second method is called ileorectal anastomosis. The large intestine and the connection between the small intestine and rectum are removed. The rectum remains in the body while the end of the small intestine is sewn to the rectum. The procedure can only be performed if there are no polyps in the rectum.
As part of the proctoelectomy, which is the third method, the entire colon and rectum are removed. The sphincter is also removed. After the anus is closed, the buttocks usually retain their shape. The patient gets a permanent artificial anus.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis of familial adenomatous polyposis is unfavorable in a large number of cases, although the disease does not lead to a reduction in average life expectancy.
The hereditary disease is caused by a mutated gene. Since legal requirements prohibit an intervention in the genetics of humans according to the current status, scientists and medical professionals cannot make any changes. This leads to a symptomatic treatment of the patient. This is done in an operative procedure. Operations are generally associated with various risks and side effects. Complications can arise that lead to secondary diseases or complaints.
The treatment plan involves removing parts of the bowel. If the operation is successful, the patient is usually left out of the treatment as cured after a few weeks or months. The end of the medical care depends on the method used. If the sphincter is retained, the patient can be discharged after the wound has healed. If an artificial anus is temporarily placed, the treatment takes several months.
With both methods, follow-up examinations take place at regular intervals. These must be adhered to until the end of life so that changes and abnormalities are noticed as early as possible. In severe cases, an artificial anus must be placed permanently. Here the patient needs lifelong medical care.
Prevention
It is difficult to prevent congenital familial adenomatous polyposis. Taking medications such as celecoxib or sulindac can help slow the growth of polyps. Nevertheless, the high risk of cancer persists.
Aftercare
With this disease there are usually very few follow-up options available to those affected. Here, the affected person is primarily dependent on an early diagnosis so that there are no further complications or complaints. Self-healing cannot occur in this disease, so medical examination and treatment should always be carried out.
As a rule, the person affected with this disease is dependent on an operation. After such an operation, the person affected should definitely rest and take care of their body. Exertion or other stressful physical activities should be avoided in order not to unnecessarily burden the body. In many cases, help and support from friends or family is very important.
Psychological support can also take place here so that there are no psychological upsets or depression. Even after a successful treatment, regular checks of the bowel are necessary in order to detect further damage at an early stage. This disease may also reduce the life expectancy of the person affected. No further follow-up measures are possible after the procedure.
You can do that yourself
Familial adenomatous polyposis offers few opportunities for self-help. The body’s natural regeneration processes are not sufficient to cure the disease.
In everyday life, care can be taken to lead a healthy life so that the organism is strengthened. Since the disease leads to colon cancer in many cases, a healthy intestinal flora should be particularly important. A balanced diet rich in vitamins that is easy to digest and does not burden the intestines should be included.
Carbohydrates and animal fats should be avoided or reduced. Dietary fiber as well as fresh fruit and vegetables are digested well by the body and strengthen the internal defense function. In addition, sufficient exercise and sport helps, as these activities promote health.
In addition to positive physical impulses, mental support is important. The psyche and the basic attitude towards life have an effect on wellbeing. Stress should be avoided or reduced as quickly as possible. It is helpful to use relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
The inner balance is established and thus makes it easier to deal with the disease and its complaints. Confrontations with other people should be reduced. Harmony, the exchange with social contacts and a wide range of leisure activities have a positive influence on the patient.